WCAG is an international standard for accessibility based on four principles.
2024/10/29

WCAG(Web Content Accessibility Guidelines is a set of standards established to ensure that websites and web content can be used fairly by as many people as possible.International GuidelinesYes. In particular,standards to make websites more accessible to users with disabilities and the elderly.As such, many countries and companies use this as a basis for ensuring web accessibility.
WCAG outlineshow websites and web content should be accessible, based on the followingFour Principles:is based on the following.。
2. Operable
3. Understandable
4. Robust
Additionally, WCAG includes three conformance levels labeled 'A', 'AA', and 'AAA' to indicate the degree of accessibility compliance.There are three conformance levels: 'A' (minimum accessibility), 'AA' (standard accessibility), and 'AAA' (highest level of accessibility).These levels demonstrate how accessible a website is.Understanding these four principles and three conformance levels allows websites to correctly comply with WCAG.。
Compliance with WCAG enhances user convenience and corporate brand value, while also minimizing legal risks.
This article will explain WCAG, including the aforementioned four principles and three conformance levels, as well as the benefits of compliance and the risks of non-compliance.
While this article explains WCAG, the following‘Web Accessibility Implementation Guidebook’ (published by the Digital Agency).provides detailed information on specific methods for WCAG compliance.Designers, engineers, and those involved in web page production should definitely refer to this article along with it.
Web Accessibility Implementation Handbook (Last Revised: March 29, 2024)
Table of Contents
- 1 The 'Four Principles' and 'Three Conformance Levels' of WCAG
- 2 Five Benefits of WCAG Compliance
- 3 Failure to comply with WCAG in Japan may result in administrative guidance or fines.
- 4 Three Case Studies of Companies and Organizations Adopting WCAG
- 5 Relationship between WCAG and JIS
- 6 With UNIWEB, immediate compliance with WCAG is possible.
The 'Four Principles' and 'Three Conformance Levels' of WCAG
First, it's essential to understand WCAG and know the four principles and three conformance levels to build web content that complies with it.
WCAG comprises four principles,each associated with multiple guidelines.This serves as a specific guideline when creating web content. And,each guideline has achievement criteria based on the three conformance levels.This forms the foundation of WCAG.
◆Structure of WCAG
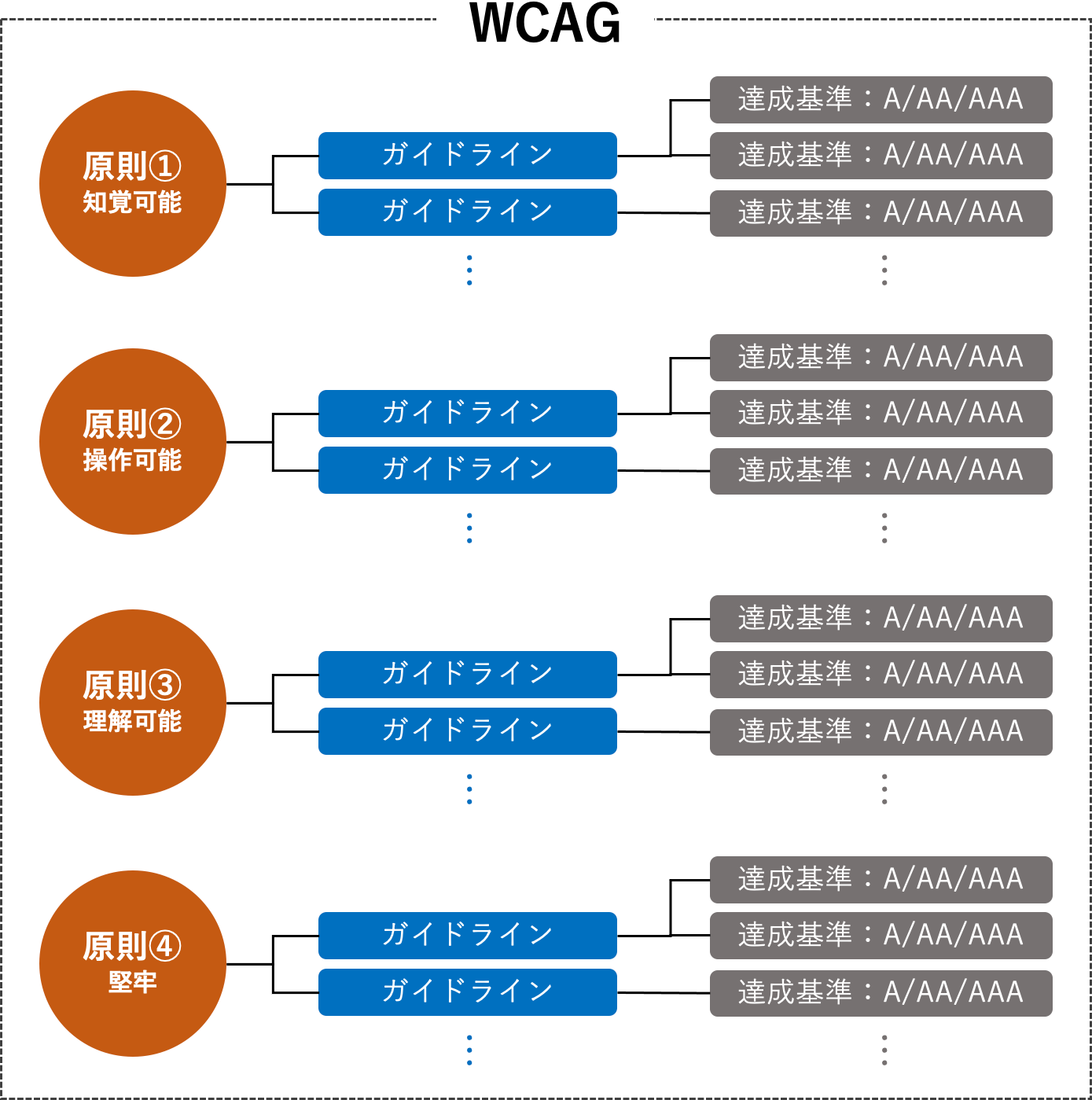
Now, let’s explain the four principles.
Four Principles: 'Perceivable', 'Operable', 'Understandable', 'Robust'
The four principles that shape WCAG arethe foundation set to make websites accessible to many users.and aim to make websites usable regardless of disabilities. Each principle will be explained in detail.
1. Perceivable (Perceivable)
This principle ensures that users can perceive web content. To allow users with visual or hearing impairments to recognize the content,information such as text, images, and audio must be provided through alternative means.This is necessary.
◆Examples of 'Perceivable':
・Information presented not relying solely on color
・Subtitles or audio descriptions for videos
In this way, allcontent must be perceivable regardless of visual or auditory limitations.This necessitates the use of text alternatives.
2. Operable (Operable)
This principle ensures that users can operate websites.It must allow users with disabilities to operate with just a keyboard or provide additional time if users cannot operate within a time limit.It must ensure that users can adequately complete operations on the content.
◆Examples of 'Operable':
・Sufficient time allowance
・Restrictions on flashing or blinking
In this principle,it is crucial for users using any devices or assistive tools to be able to operate the content.Therefore, designing for this is very important.
3. Understandable (Understandable)
This principle ensures that all users can understand content and interfaces.It should avoid overly complex operations and difficult terminologyand be designed to be intuitive and easy to understand for users.This is necessary.
◆Examples of 'Understandable':
・Clear error messages
・Use of clear and simple language
To avoid confusing users and ensure they can understand,it is important to avoid jargon and complex phrasing, presenting content flow and functionality clearly and understandably.。
4. Robust (Robust)
Content must be robust and function well across various technologies and devices, meaningit should be designed to ensure compatibility.When users utilize assistive tools or browsers they currently use or may use in the future, it should work without issues.This is a principle. Users should be able to access the content seamlessly using tools or browsers they are currently using or may use in the future.that may appear in the future. Therefore,using standard-compliant code.This enables users to access content without issues.◆Examples of 'Robust':
・Use of accurate HTML
・Maintaining compatibility across various browsers and devices
To ensure that the site can accommodate many users for the long term, it must be designed to be technically robust and flexible.
It is essential to validate and construct websites based on these four principles.
Currently, WCAG 2.0, which has become an international standard, features abstract content that does not rely on technical specifications, enabling easy and efficient validation.This design is notable for enabling numerous websites to be validated easily and efficiently (testability) amidst rapid changes and advancements in technology and devices.
Three Conformance Levels: 'A', 'AA', 'AAA'
Under the four principles mentioned earlier, multiple guidelines are established for each principle, providing detailed criteria to make web content as accessible as possible for users.
Additionally, each guideline has several achievement criteria classified into three levels of conformance: A to AAA. These conformance levels indicatehow much accessibility consideration the website has.These achievement criteria help in determining whether a website conforms to accessibility standards upon validation.
1. Conformance Level A (Minimum Accessibility Standards)
Conformance Level A means that the basic accessibility requirements are met. At this level,only the minimum accommodations for users to access contentare made. For example,providing alternative text for images and stopping auto-play for videos are included.Websites that do not comply with Conformance Level A risk making basic operations impossible for many users, thusshould be addressed as a top priority..
2. Conformance Level AA (Standard Accessibility Standards)
Conformance Level AA is a standard accessibility criterion that meets requirements for a broader range of users.Compliance at this level is recommended by many countries and companies for web content.For example,maintaining appropriate color contrast or labeling input fields clearly.By complying with Level AA, the website becomes accessible to the majority of users.
3. Conformance Level AAA (Highest Level of Accessibility Standards)
Conformance Level AAA meets the highest accessibility requirements. Compliance at this level allows almost all users with disabilities to comfortably access content.Providing sign language videos and maintaining clear concise text, among others.However,achieving this level is not always realistic, so it is not recommended as a requirement.
In this way, it is divided into three levels from A to AAA.To meet AA standards, A must be satisfied, and to meet AAA standards, both AA and A must be met.Meeting AAA standards is highly challenging, and as of now,the recommended goal in web accessibility compliance is to achieve 'Conformance Level AA'.It is said.
Furthermore, guidelines regarding achieving Conformance Levels AA and A are available.The Web Accessibility Infrastructure Committee (WAIC) publishes quick reference tables,Please refer to this alongside.
JIS X 8341-3:2016 Achievement Standards Quick Reference (Level A & AA)
Next, let's discuss the benefits of complying with WCAG.
Five Benefits of WCAG Compliance
Complying with WCAG offers numerous advantages for websites. Here are five specific benefits.
Benefit 1: Improved Accessibility and UX
By complying with WCAG, overall site accessibility improves, enhancing usability not only for people with disabilities but for all users. This leads tomore users being able to enjoy a comfortable experience, thereby enhancing UX (User Experience).
For instance, providing alternative text, designing with color-vision deficiencies in mind, and ensuring keyboard navigability,improvements for accessibility enhance the web experience for all users, regardless of disabilities.Such measures make navigation easier for users on the site without confusion,resulting in decreased bounce rates and increased dwell time and conversion rates.
Improving accessibility directly correlates with enhancing UX, providing a comfortable and seamless operation for all users,an important means to increase customer satisfaction.That's right.
Benefit 2: Enhanced Brand Image
Being considerate of accessibility demonstrates a commitment to social responsibility and enhances the brand image of companies and organizations, especially intoday's environment where inclusivity and diversity are emphasized in companies, becoming a major factor in building social trust.
This improves the company's reputation and earns trust from customers.It makes it more likely for customers to choose their services and contributes to expanding their customer base.。
Benefit 3: Reduced Legal Risks
Many countries and regions have strengthened laws and regulations regarding web accessibility. For example,the U.S. ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) and the EU Web Accessibility Directive.These levels demonstrate how accessible a website is.In Japan, the 'Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities' mandates the provision of reasonable accommodations.
Compliance with WCAG helps meet these legal requirements and avoid legal risks and troubles.
Benefit 4: Compatibility with New Support Tools and Devices
WCAG is based not only on traditional web technologies but also on universal design principles.Thus, it is compatible with not only current accessibility tools and devices but also with tools and devices that will evolve in the future.
For example, assistive tools such as screen readersanalyze content based on HTML tags and ARIA attributes.Therefore, if appropriate labels and ARIA attributes are correctly applied to the text based on WCAG, even as screen reader technology evolves, the website can be accurately interpreted and provide the necessary functionality to users.
Additionally, wearable devices and IoT devices access websites via web browsers or specific applications. In such cases, first, content is parsed by the browser or application, displaying it in a format suitable for the device.Thus, if an HTML structure is based on WCAG, the content will be displayed correctly, regardless of the device used.
In this way, by complying with WCAG, websites can maintain stability and flexibility without having to make sudden adjustments with each emergence of new technologies.They can continue to maintain long-term stability and flexibility.
※ ARIA attributes are HTML attributes used by assistive tools like screen readers to correctly interpret elements on web pages.
Benefit 5: Positive Effects on SEO
By complying with WCAG, websites becomemore easily indexed (registered in databases) by search engines.For example, setting alternative text for images and structuring HTML appropriately allows search engines to accurately understand the content. Therefore, improving web accessibility is essential forcontribute to higher rankings in organic search results and lead to increased traffic.
By complying with WCAG, you can enjoy numerous benefits. Now, let's discuss the risks of non-compliance, that is,the risks associated with neglecting accessibility compliance.the following explanation.
Failure to comply with WCAG in Japan may result in administrative guidance or fines.
In Japan, due to the amendment of the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, starting from April 2024,the provision of reasonable accommodations for private companies will be legally mandated.This leads towebsites will be required to implement WCAG-compliant web accessibility measures.
Currently,there are no direct penalties established for non-compliance with web accessibility.However, if websites are neglected without compliance, there is a possibility of receiving guidance from authorities. Furthermore,if improvements are not observed despite following that guidance or if false reports are made, a fine of up to 200,000 yen may be levied.For more details, please refer to the following Cabinet Office FAQ.
Moreover, even if there are no legal penalties,in today's diverse society, scrutiny of companies and services that neglect reasonable accommodations is increasing.In particular, such social trends are prominent abroad, and lawsuits related to these issues have significantly increased.
Examples of Lawsuits in the United States
In the previous section, we mentioned the U.S. ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act), which is a human rights law protecting the rights of individuals with disabilities and includes accessibility-related provisions. In recent years in the U.S.,Cases where companies' websites are sued for not meeting accessibility requirementsare on the rise.
For example, the supermarket chain "Winn-Dixie" was sued because users with visual impairments were unable to use screen readers to order products on their e-commerce site.
The court determined that Winn-Dixie's website is considered a "public space" and therefore must comply with ADA accessibility requirements, ordering Winn-Dixie to modify the website to ensure that visually impaired users can correctly utilize it with screen readers.
Another example is the official website of popular artist Beyoncé (beyonce.com), which was sued for not being compatible with screen readers for visually impaired users and "restricting access for visually impaired individuals." As a result, the site improved its accessibility and changed to a design compliant with WCAG following the lawsuit.
In this way,Abroad, regulations have progressed to the point where non-compliance with WCAG poses realistic litigation risks.。In Japan, where the provision of reasonable accommodations has been legally mandated, it is quite conceivable that similar cases may arise in the future.Therefore, companies need to also consider these risks in their responses.
Next, let’s introduce companies and organizations that comply with WCAG.
Three Case Studies of Companies and Organizations Adopting WCAG
Recently, an increasing number of companies and organizations have adopted WCAG to reach a broader range of users and improve UX. Here, we present three representative examples.
Case Study 1: Apple
Apple has been an early adopter of WCAG-compliant web content as a pioneer in accessibility.Its website and products are equipped with accessibility features to accommodate people with visual impairments, hearing impairments, and limited mobility.For example, they offer visual support features such as screen reader compatibility and contrast adjustments.
Reference: Accessibility – Apple
Case Study 2: Microsoft
Microsoft is also a company that has achieved web accessibility in compliance with WCAG.The company works to ensure that its products and services are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, through a methodology called "Inclusive Design."In particular, its official website and cloud services (such as Azure) are designed to support keyboard navigation and provide voice guidance features for visually impaired users.
Reference: Microsoft Inclusive Design、Microsoft Azure
Case Study 3: Cabinet Office
The Cabinet Office's website iscompliant with "Level AA" of JIS X 8341-3:2016, which is equivalent to WCAG 2.0 (Japanese web accessibility standards: see below).It also accommodates some areas for "Level AAA" compliance as possible. (Old content and externally provided PDF files are exceptions as they are difficult to modify.)
The Cabinet Office's website isParticularly as a public institution, it is required to maintain high standards, so it continuously conducts verification and improvements.For newly created or updated pages, efforts are made to comply with Level AA.
Reference: Cabinet Office Web Accessibility Policy
Next, we will explain the relationship between the international standard WCAG and the domestic standard JIS.
Relationship between WCAG and JIS
WCAG was first published in 1999 as WCAG 1.0, andWCAG 2.0 is now the international standard (ISO).It is said.
WCAG is an international web accessibility standard, butin Japan, "JIS X 8341-3:2016" has been established as the equivalent standard to WCAG 2.0.JIS X 8341-3:2016 incorporates nearly all the content of WCAG 2.0, and its basic structure (four principles and three compliance levels) also aligns with WCAG.
It serves as a guideline for Japanese public institutions and companies to ensure web accessibility,playing an important role in promoting the spread of web accessibility by translating international standards into local regulations.。
As mentioned earlier, WCAG 2.0 is currently the international standard, and it is equivalent to JIS X 8341-3:2016, butin fact, WCAG itself has undergone content updates since 2.0, with WCAG 2.2 already published and WCAG 3.0 in the draft stage.
◆Relationship between WCAG, ISO and JIS
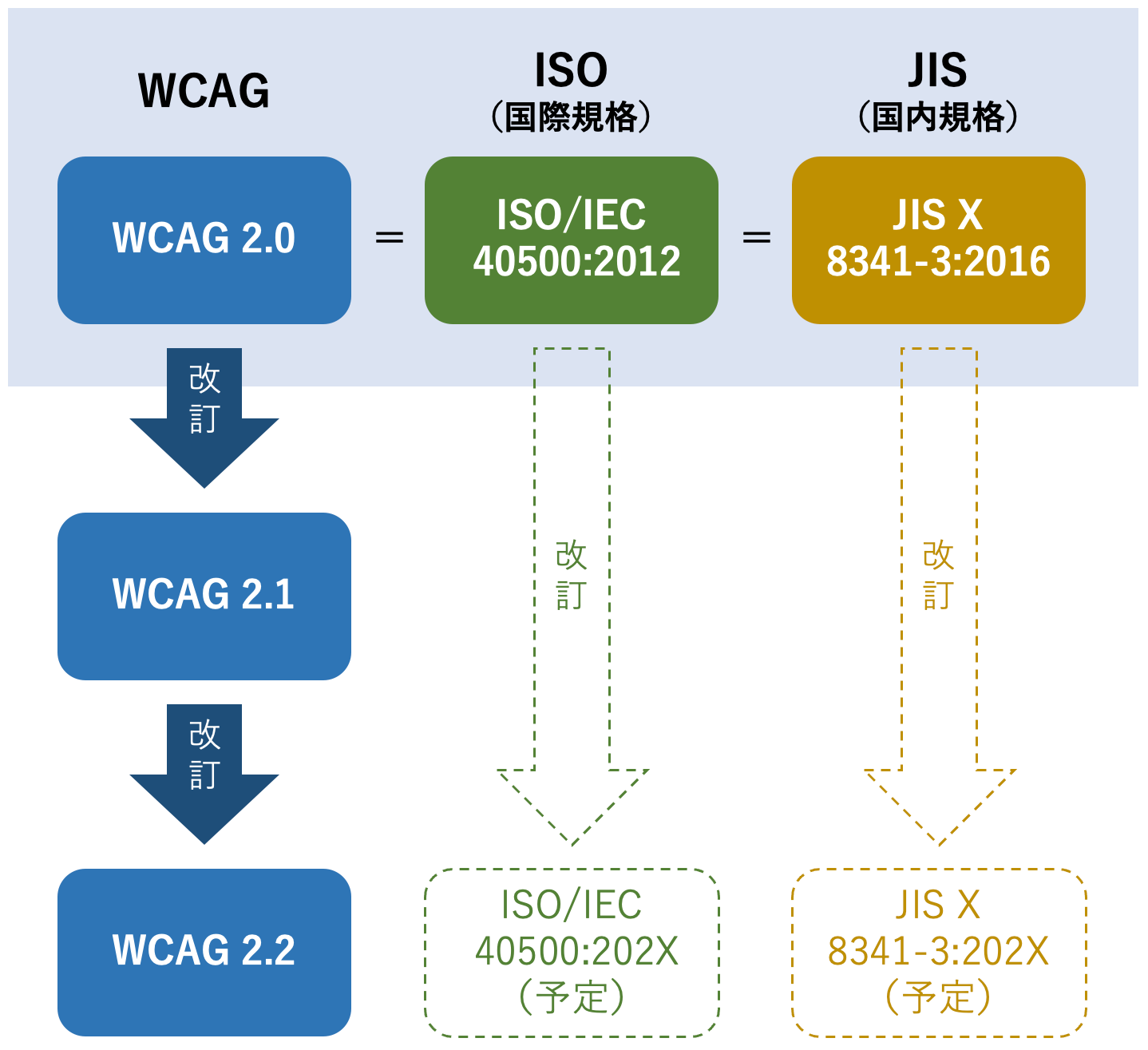
As mentioned above, preparations are currently underway to revise ISO and JIS standards in response to WCAG 2.2.
WCAG 2.1 and 2.2 strengthen accessibility for mobile devices.
Here, we will explain "WCAG 2.1," the higher version of WCAG 2.0, and the latest version, "WCAG 2.2."
First of all, WCAG 2.1 isdue to the proliferation of smartphones and tablets,accessibility on mobile devices has become necessary,in response to which, particularlystandards for accessibility for touch operations and small screens have been strengthened.。
In WCAG 2.1, 17 achievement criteria focused on mobile responsiveness, visual disabilities, and cognitive impairments were added. (Including the 61 achievement criteria of WCAG 2.0,2.1 has a total of 78 achievement criteria.)
And in the latest WCAG 2.2, 9 achievement criteria have been added, particularly aimed at improving accessibility for users with cognitive disabilities and the elderly, focusing on the use of mobile devices. (Adding to the 78 achievement criteria of WCAG 2.1,2.2 brings a total of 87 achievement criteria.)
Specifically, the following criteria have been added:
◆Representative additional criteria
・Limiting the complexity of gestures(WCAG 2.1): Ensuring that simple gestures can be used for operation.
・Providing multiple input methods(WCAG 2.1): Recommending designs that prevent erroneous operations due to taps or clicks.
・Zoom support for content(WCAG 2.1): Ensuring that content remains intact when the screen is enlarged.
・Focus visibility(WCAG 2.2): Making keyboard focus clearly visible.
・Target size(WCAG 2.2): Ensuring a minimum size for click or tap targets to reduce erroneous operations.
・Authentication that does not rely on memory(WCAG 2.2): Providing methods for password authentication that do not require memory (such as biometric authentication).
In this way,In the transition from WCAG 2.0 to WCAG 2.2, the emphasis has been placed on strengthening accessibility for mobile devices.This is a key point.
With UNIWEB, immediate compliance with WCAG is possible.
This article provided a detailed explanation of WCAG. With the revised Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, it has become essential for all websites to address web accessibility. As a result,designers, engineers, and maintenance staff are required to have a correct understanding of WCAG and prompt responses for their own websites.
If you are considering building a WCAG-compliant website, we recommend our‘UniWeb’This tool is a plugin that easily implements various functions to enhance web accessibility and create user-friendly websites for all users.It supports WCAG 2.1 and JIS X 8341-3:2016, contributing to reduced legal risks and improved usability.
The response to WCAG, which can incur high costs and take months, can also besignificantly reduced by using Uniweb, as it only requires adding a single line of code to the website, thus minimizing financial and time costs.。The pink circular icon located at the bottom right of this articlewill allow you to experience the functionalities of Uniweb, so please give it a try.
Additionally, methods for specifically addressing web accessibility and tools that can be utilized have been outlined in the following articles, so please read along with this article.
Related Articles:What web accessibility measures must site managers implement?
-
Contact Us
-
Request Info
-
Free Trial
-
Partner System







