Explaining the GRI, the disclosure standard for sustainability reporting, from the ground up.
2025/05/20

GRI(Global Reporting Initiative)is an international non-profit organization dedicated to supporting sustainability reporting by companies and organizations,Widely used around the world as a standard for ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) information disclosureGRI Standard."The formulating body of the.
This GRI Standard, provided by GRI, is,Practical standards for companies to report their sustainability efforts in a transparent and comparable manner to stakeholdersand many global companies areFoundation for Report WritingIt is employed as a
◆GRI and GRI Standards
| GRI(Global Reporting Initiative) | GRI Standards | |
| entity | nonprofit organization | Reporting guidelines developed by GRI |
| Role and Contents | Organization promoting the dissemination and standardization of sustainability reporting | ESG information disclosure standards themselves ("what" and "how" to report) |
| how it's being used | GRI compliant" => means in accordance with the standards issued by this organization. | Uses GRI Standards" => specific framework used in actual disclosures |
| Frequency of updates | Little change in the organization itself. | Revised periodically (e.g., major revision in 2021) |
Some companies have enhanced the credibility of their reporting based on these GRI standards, while delving deeper into key topics such as "climate change," "human rights," and "governance.
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of the GRI Standard, including its structural features, background to the attention it has attracted, examples of actual corporate applications, and differences from other frameworks.
Table of Contents
- 1 Basic Structure of the GRI Standard
- 2 Background of GRI's Attention and Reasons for "Standardization
- 3 Practical examples of companies using the GRI Standards
- 4 Differences between GRI and other disclosure frameworks and how to use them
- 5 Conclusion
Basic Structure of the GRI Standard
When companies report sustainability information, "what items should be organized and in what framework?The GRI Standards are widely adopted as international guidelines for this purpose.
The GRI Standards, developed by the GRI, are international standards for corporate ESG information disclosure,Corporate social responsibility, environmental considerations, governance, and other initiatives (ESG) are to be disclosed to stakeholders in an easy-to-understand and comparable form.。
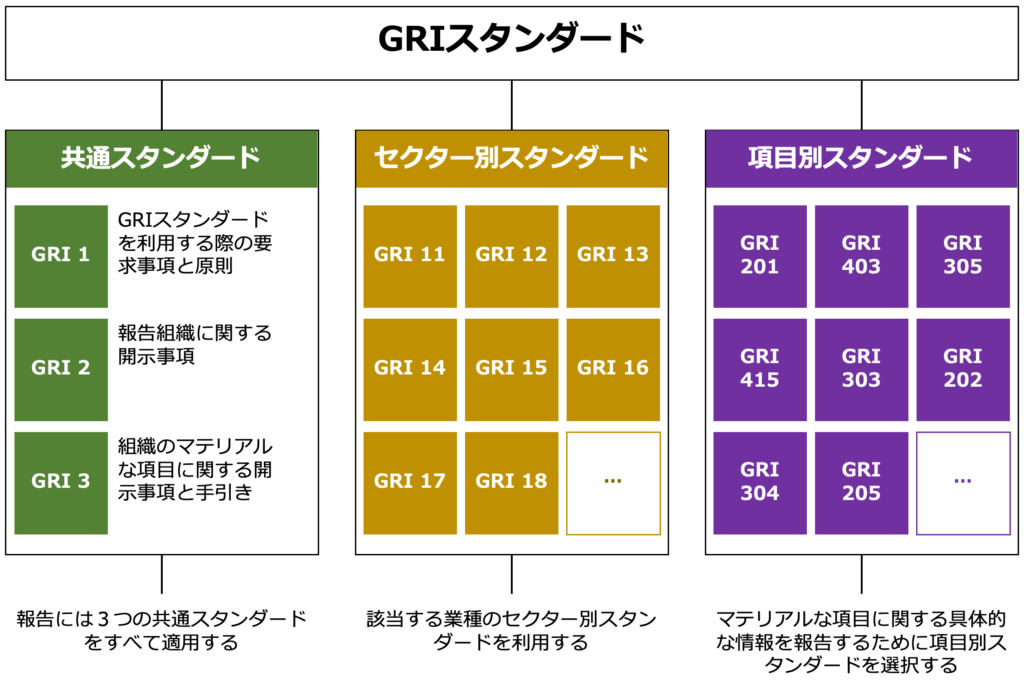
The GRI Standard consists of the following
◆GRI Standard Structure
Citation: Introduction of ESG Disclosure Framework (JPX)Created based on the figure shown.
The GRI Standards are largelyThree elementsIt is composed of
Basic disclosure items used by all reporting companies, including an overview of the organization, reporting methodology, identification of materiality issues, and stakeholder relationships.
Sector Standards
Examples include mining, oil and gas, agriculture, and banking, with more to come.
Topic Standards
Disclosure standards related to specific topics such as environmental, social, and governance, e.g., "water use," "workplace safety," "anti-corruption," etc., which are used selectively depending on the materiality analysis.
In this way,Three-tier structure consisting of common criteria (GRI 1-3), sector criteria by industry, and topic criteria by itemand allows for flexible disclosure according to the characteristics of the company and its industry.
For example, a company in the manufacturing industry would focus on topic standards related to "energy consumption" and "waste management," while a company in the financial industry would be required to disclose information on "human rights considerations of portfolio companies," "indirect environmental impacts," and other industry-specific risks.
The GRI Standards function as a constant common framework around the world, while being flexible enough to accommodate such diverse industries and issues.
The following section will explain the background and reasons why the GRI has become so widely accepted as a "global standard" and why it is attracting so much attention.
Background of GRI's Attention and Reasons for "Standardization
In this report, we will explain in detail why GRI has become so widely accepted and positioned as the global standard for sustainability reporting, as well as the background to its high profile and "standardization.
Background and Purpose of GRI's Establishment
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) was established in 1997 by the U.S. non-profit organization CERES (Coalition for a Sustainable Economy) and the Tellus Institute.
The background,There was a growing concern about corporate environmental responsibility, such as the Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989.The
At the time, there were no clear standards for measuring corporate social responsibility or environmental performance, and stakeholders had limited means to evaluate corporate actions.Transparency of non-financial information."The company was established for the purpose of realizing
Later, in 2002, theStrengthened cooperation with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)and was officially inaugurated as an independent organization at UN headquarters in the same year.
With this, GRI has further increased its international recognition and has begun full-fledged efforts to create a standard for sustainability reporting.
Three Reasons Why GRI Has Become a Global Standard
The GRI is more than just a set of guidelines for one organization; it has become the global standard for sustainability reporting, due to a combination of multiple institutional, practical, and international factors.
Three reasons of particular importance are explained below.
Reason #1: Legitimacy through collaboration with international organizations
GRI entered into a strategic partnership with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in 2002 and gained international recognition at the Johannesburg Summit (Earth Summit) in the same year.
After that.By deepening cooperation with the OECD, ISO, the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), and other organizationsThe company has built global credibility and legitimacy.
Reason #2: Practical response ahead of others and evolution of guidelines
GRI isFirst edition of the GRI Guidelines published in 2000.The company was one of the first to provide a mechanism for companies to actually create reports.
In particular,A framework to support the entire reporting process, including materiality identification and stakeholder engagementis highly regarded for its deeply rooted content in corporate practice.
Reason #3: Widespread adoption by government and business and institutional establishment
The GRI Standards have been adopted by government agencies, stock exchanges, and major corporations from early on, particularly in Europe.
In particular,The EU's Non-Financial Disclosure Directive (NFRD) has also had an impact, for example, on theand by its increasing incorporation into the public system,A "substantial criterion" for a companyIt became established as a
Today, the recognition that "first of all, disclosure should be made in the GRI" has become widespread in the practical field.
Three key points that companies and investors look to GRI
The GRI standards have been widely adopted not only because of institutional requirements, but also because they are a good fit for both companies and investors.Ease of use and reliability.These levels demonstrate how accessible a website is.
There are three points where GRI is particularly valued from a practical standpoint
◆Three points that companies and investors pay attention to GRI
(ii) Disclosed information"Comparative Possibilities"The ability to guarantee the
③ "Transparency"A built-in reporting process with a high degree of
These features make the GRI Standards a highly practical and reliable framework for sustainability information disclosure.
Backed by collaboration with the United Nations and governments,The fact that it is a globally recognized standard makes it easier to ensure the legitimacy of the content of the report.For companies, theEasy to gain trust from external stakeholdersThis has the advantage that
Also, by clearly specifying specific disclosure indicators,Comparison with other companies in the industry and investment decisionsThe format is easy for investors to analyze.
Furthermore, the disclosure of not only the mere reporting of results, but also the process of selecting issues and the involvement of stakeholders, is a key feature of the project, making the transparency of the corporate decision-making process more visible.
Practical examples of companies using the GRI Standards
This section introduces actual examples of how companies are using this framework and incorporating it into their own sustainability reporting, as well as examples of companies that have published GRI-compliant reports.
Case 1: Toyota Motor Corporation features systematic use of GRI Standards in its Integrated Report
Toyota Motor Corporation communicates its sustainability initiatives in the form of an integrated report and a sustainability data book, in which the GRI Standards are disclosed by reference.
The company reports,GRI Content Indexand clearly state theWe carefully tie our company's corresponding page to each disclosure item specified by GRI.This allows stakeholders to gain a systematic and comprehensive understanding of Toyota's non-financial information.
In particular, we disclose specific figures and policies on environment-related items (greenhouse gas emissions, water resources, waste management, etc.) and themes related to human rights and labor, while utilizing the GRI Topic Standards.
Toyota also through materiality analysis,In accordance with GRI 3 (Disclosure on Materiality), we also explain the reasons for the selection of priority issues and their relationship with society.。
This consistent reporting style has earned the company a strong reputation for its ESG information among international investors.
Reference: Sustainability Data Book 2024、GRI Content Index(TOYOTA)
Case 2: Unicharm strengthens its practices by identifying issues based on GRI 2 and GRI 3
Unicharm Corporation discloses information in accordance with the GRI Standards in its Sustainability Report 2024.
The company has published a "GRI Standard Comparison Chart" to clearly indicate the status of its response to each GRI item, in particular,Focus on disclosures related to GRI 2 (General Disclosure) and GRI 3 (Material Topics)and provides the following information
Disclosure Information on GRI 2 and GRI 3
Details of the organization, reporting period, frequency of reporting, and contact information.
Scope of sustainability reporting and reporting entities.
Governance structure and composition; roles and responsibilities of the highest governance body.
GRI 3: Material Items
Process for identifying critical issues and why.
Policies, initiatives, and performance indicators for each key issue.
In addition, the company has「Kyo-sei Life Vision 2030」This information is detailed on the company's sustainability website and in its Sustainability Report 2024.
Reference: Sustainability Report 2024(Unicharm Group)
Case 3: "Nestlé" uses both GRI standards and its own framework to improve transparency
Nestlé, along with the adoption of the GRI standard,Unique "Creating Shared Value (CSV: Creating Common Value)" frameworkThe company is building aBy utilizing the two in a complementary manner, we are able to achieve highly transparent reporting that balances corporate strategy with international reporting standards.
The company's "Creating Shared Value and Sustainability Report 2023" clearly states that the report complies with the GRI Standards and provides a detailed "GRI Content Index" separately, which organizes the corresponding pages, disclosure methods, and reasons for each disclosure item, focusing on GRI 2 (general disclosure) and GRI 3 (materiality-related).
What makes Nestlé unique is its focus on visualizing materiality assessments.
The report mapped the key issues for the company on two axesMateriality Matrix."was published in the magazine,Visually organized according to the GRI 3 process to show which issues are being addressed and how。
◆Materiality Matrix
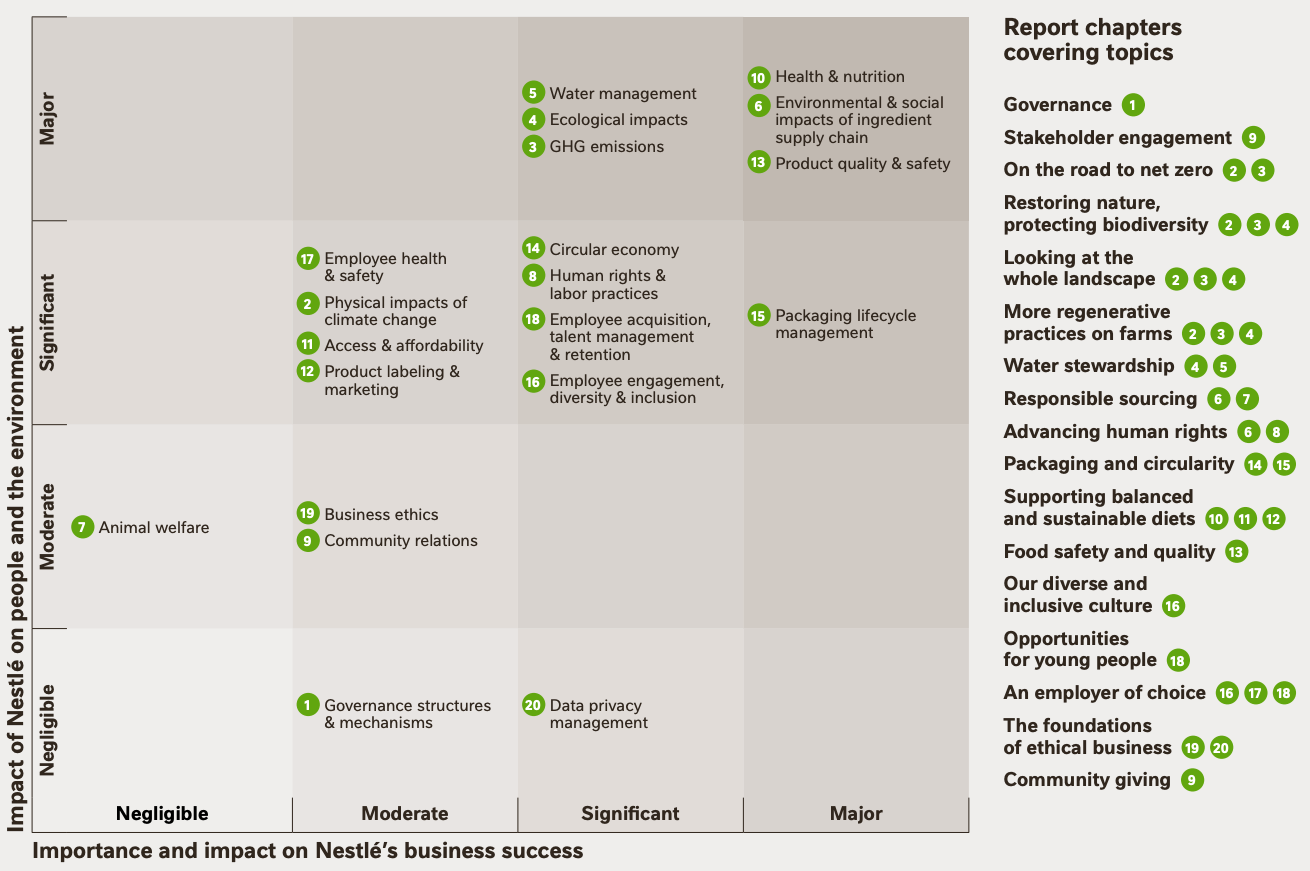
出典:Creating Shared Value and Sustainability Report 2023
This allows us to consistently communicate to stakeholders the background of why we are focusing on the issue.
In addition, Nestlé is not only a GRI in sustainability reporting.It is also compliant with the SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) and TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures).The company is strongly committed to utilizing multiple criteria in an integrated manner.
Reference: Creating Shared Value and Sustainability Report 2023(Nestlé)
In this way, each company flexibly utilizes the GRI Standards according to their respective industries and strategies to visualize their ESG issues and policies.
What do these companies have in common?Strategically determine "what standards to use and how to communicate them" rather than simply complying with the GRIThe point is that we are doing so.
Especially for global companies, in addition to GRI, SASB, TCFD, and even ISSBUse with other frameworksWe are working to build trust with investors and society while
The next chapter describes the relationship between GRI and other ESG disclosure frameworks that are often compared to GRI and summarizes the different characteristics and roles of each.
Differences between GRI and other disclosure frameworks and how to use them
In disclosing ESG information, not only the GRI Standards,SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board)、TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures)and the newISSB (International Sustainability Standards Board)Several frameworks exist, including
At first glance, these standards may seem like similar guidelines, but in reality they differ in terms of target audience, purpose of disclosure, and nature of information to be emphasized.
In order for companies to select and use the appropriate frameworks together, they must understand the characteristics of each and use them strategically according to their own situation and reporting objectives.
Please see below for a list of the differences between the four main frameworks.
◆Comparative table of representative ESG disclosure frameworks
| target reader | Points to be emphasized | Main Features | |
| GRI | Overall Stakeholders | Attitude of clearly stating social and environmental impacts | An international standard for sustainability reporting, specifying indicators for each issue. |
| SASB | investor | Financial Impact | Defines important ESG items by industry, emphasizing relevance to financials. |
| TCFD | Investors and regulators | Climate Change Risk | Recommendations for disclosure of climate-related financial risks and opportunities, consisting of four items. |
| ISSB | investor | Financial Relevance | Under construction as IFRS S1/S2*, an integrated, global disclosure standard. |
※
IFRS S1: General rules for disclosure of ESG-related information in general, defining disclosure requirements for governance, strategy, risk management, etc.
IFRS S2: Detailed standard for climate change-related disclosures, based on the TCFD framework but with greater emphasis on financial relevance.
While the GRI Standards have been adopted by many companies as the international framework for ESG disclosure, they are not complete in themselves; in recent years, more and more companies are using multiple disclosure frameworks in tandem to meet the needs of investors and regulators.
For example, Nestlé and Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, among others, have responded to guidelines such as SASB and TCFD in addition to GRI, complementing the breadth and depth of their disclosures with the characteristics of each.
The reason why multiple frameworks are needed, then, is that the recipients of ESG information are not uniform and differ in what they consider important.
What GRI focuses on, though, is the "impact perspective" of how a company is affecting society and the environment,SASB and ISSB focus primarily on the "financial relevance" of how those impacts relate to the company's finances。
◆Different perspectives
GRI: In addition to financial impact, focus on social and environmental impact(Double Materiality)
Relying on a single criterion without understanding these differences may lead some readers to conclude that the required information is lacking.
Especially for publicly traded companies and those operating in global markets,Financial-related disclosures such as TCFD and ISSB with investor relations in mind are also essential.
Conclusion
The GRI Standards are widely adopted as the international standard in sustainability reporting, regardless of industry or company size,Strong framework for systematic disclosure of ESG informationWe provide.
In particular, the explicit social and environmental impact perspective and the flexible structure based on materiality are practical advantages for many companies.
It is also being used in conjunction with other frameworks such as SASB, TCFD, and ISSB, and the GRI serves as a complementary foundation for them.
In the future, the ability to appropriately use multiple criteria for different purposes will be important for corporate credibility and transparency.
-
Contact Us
-
Request Info
-
Free Trial
-
Partner System