Key Points of the 'Revision of the Disability Discrimination Elimination Law' Explained in 10 Minutes
2025/11/19

Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities(Officially known as the Act on Promotion of Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, this law was enacted in June 2013. According to the Cabinet Office's website, its objective is to 'promote the elimination of discrimination based on disability, in order to realize a society where all citizens respect each other's personalities and individuality without being discriminated against based on the presence or absence of disabilities.' In simple terms,'Prohibiting discriminatory acts based on disability and demanding the provision of reasonable accommodations.'is the kind of law that relates to such topics.
The subjects of this law include public institutions and private businesses such as companies and stores, and it does not impose penalties on individuals. However, in today's society where diversity is prioritized,it is necessary for each citizen to correctly understand disabilities and create a society where discrimination and unfair treatment do not exist.is being sought.
ThisAct on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities was amended in 2021, and the amended law will be enforced from April 2024.However, as of 2025, many businesses are still wondering, "What has actually changed?" and "What is reasonable accommodation?
The focus of this revised law is as follows
This article will explain in detail the key points of this amendment to the Law for the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, and what should be implemented or prohibited in accordance with the amended law, with examples provided.You can understand the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities in 10 minutes, so business operators are encouraged to refer to this.
We will also discuss how the revised law is being received now that more than a year has passed since its enactment.
Table of Contents
- 1 The key point of the amendment to the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities is the 'obligation to provide reasonable accommodation'.
- 2 Five Key Points of the Obligation to Provide Reasonable Accommodation
- 3 Specific Examples of Prohibited 'Unjust Discriminatory Treatment'
- 4 Examples of Providing Reasonable Accommodation
- 5 Provision of 'Reasonable Accommodation' on Websites
- 6 There are no immediate penalties for violations, but there is a possibility of administrative guidance.
- 7 Less than 40% awareness of the revised law one year after its implementation
- 8 Conclusion
The key point of the amendment to the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities is the 'obligation to provide reasonable accommodation'.
In recent years, there has been a growing global interest in the rights of persons with disabilities, as seen in the promotion of the SDGs. In Japan, there has been an increasing awareness among companies regarding compliance, and the approach to persons with disabilities has become a priority. In this context, the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities was amended in 2021, and the amended law is set to be enforced from April 2024.
As mentioned earlier,The two main points of the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities are:.
1. Prohibition of discrimination and unfair treatment against persons with disabilities.
2. Provision of reasonable accommodation.
Furthermore, what was reviewed in the amendment of the law in 2021 is thatthe 'provision of reasonable accommodation', which has been an effort obligation for businesses, has been changed to a 'legal obligation'.
◆ Change of the Provision of Reasonable Accommodation from 'Effort Obligation' to 'Legal Obligation'
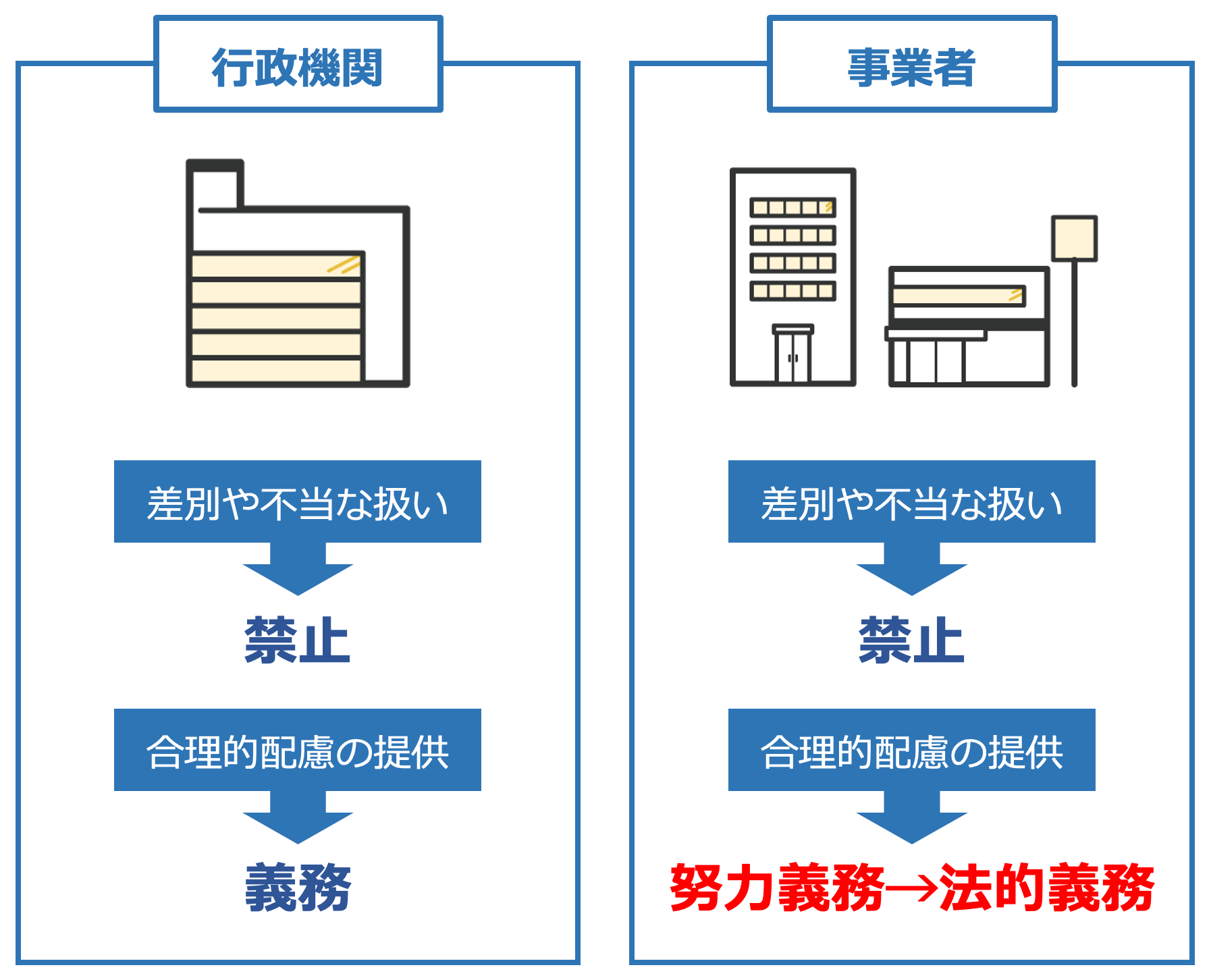
In other words,The change from 'making efforts to provide' to 'must provide' is the key point of the amended law.As a result,companies are required to review and improve their production activities, services, employment, and working environments based on a correct understanding of persons with disabilities.This is necessary.
In the following section, we will provide a more detailed explanation of the amended Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities.
Five Key Points of the Obligation to Provide Reasonable Accommodation
In order to understand the amended Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities, it is necessary to first correctly know 'what is the provision of reasonable accommodation?' Here, for the understanding of reasonable accommodation,Five Key PointsWe will focus specifically on explaining this in detail.
Point 1: Definition of Reasonable Accommodation
According to the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, reasonable accommodation is defined as 'necessary and appropriate modifications and adjustments made to ensure that persons with disabilities can enjoy or exercise all human rights and fundamental freedoms on an equal basis with others, which are required in specific cases and do not impose a disproportionate or undue burden.'
To put it more simply, when a person with a disability utilizes a facility or service, it involves removing or altering barriers within a reasonable range according to individual circumstances, andmaking adjustments or changes to remove barriers within a range that does not impose an excessive burdenis what is required of businesses, etc. In other words,'Taking into consideration the needs of each individual with a disability and making necessary changes to the environment as much as possible to facilitate their participation in society'is the definition of reasonable accommodation.
Point 2: Consideration of Excessive Burden
The 'excessive burden' mentioned in Point 1 is specifically considered bythe extent of the following six elements:This is something that should be taken into consideration.
2. Degree of difficulty in implementation (physical, technical constraints, human constraints, etc.)
3. Costs and Extent of Burden
4. Size of the business
5. Financial Status of the Company
6. Availability of public support
Businesses should comprehensively assess whether these elements constitute an excessive burden and implement improvements within a range that does not impose a burden. However,if it is likely to be a burden, they need to explain this and the reasons to persons with disabilities.
Reference: Guidelines for Reasonable Accommodation (Overview) (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
Point 3: Scope of Obligation
The provision of reasonable accommodation has originally been a legal obligation for national and local government bodies, while it has been considered an effort obligation for private enterprises. However, due to the recent legal amendment,Private companies are also now subject to legal obligations.Here, private companies refer to:regardless of profit or non-profit, corporations, or individuals,、all types of businesses including schools, companies, stores, and hospitals will now be subjected to this obligation.This is the strategy of corporate communication.
Point 4: Implementation Methods
When providing reasonable accommodation, it is generally necessary to follow these steps:
Step 1. Understanding the Needs of Persons with Disabilities
When a request for reasonable accommodation is made by the individual with a disability, their family, or supporters, a hearing will be conducted to understand the specific needs and difficulties, and to determine what type of accommodation is necessary.
Step 2: Consideration of Specific Measures for Reasonable Accommodation
Practical accommodation methods will be considered and presented to the individual with a disability. For instance, specific measures may include removing physical barriers, modifying information provision methods, and improving communication methods. Additionally, seeking advice from disability support professionals or consultants can be beneficial as needed.
Step 3: Implementation of Specific Measures
Implement the determined specific measures. This includes making facilities barrier-free and installing appropriate signage. Necessary features will also be implemented in web content, such as providing Braille, audio guides, sign language interpretation, and reading software.
In the work environment, measures include flexible working hours, adjustments to tasks and procedures, and the installation of workplace facilities that consider disabilities.
Step 4. Evaluation and Improvement After Implementation
We will regularly receive feedback from persons with disabilities to determine whether the reasonable accommodations provided are appropriate. We will evaluate the effectiveness of the accommodations provided and implement improvements as necessary. It is essential to continually review and adjust the content of reasonable accommodations in accordance with the needs of persons with disabilities and changes in the environment.
Step 5: Education for Company Staff
Educate all employees on the importance of reasonable accommodation and specific methods for provision based on the steps outlined thus far. This will include fundamental knowledge about disabilities, the necessity of accommodation, and actual response methods.
Step 6. Establishing Consultation Desk
The provision of reasonable accommodations should not be one-sided. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a contact point where persons with disabilities, their families, or employees can consult about reasonable accommodations, ensuring that a communicative environment is always available.
In this way,a series of processes from individual consultation to the implementation of specific accommodations and feedback must be undertakenit is necessary, and businesses must prepare and establish appropriate systems.
Point 5: Support System
When providing reasonable accommodation, it is also important to strengthen cooperation with local disability support organizations and administrative bodies and to establish a support system. Additionally, as a financial support system,there are subsidies for the employment of persons with disabilities and grants for providing reasonable accommodation from local governments.There is financial assistance available to help cover some of the costs necessary for implementing specific measures, so businesses should actively take advantage of this.
Specific Examples of Prohibited 'Unjust Discriminatory Treatment'
Under the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities, companies are required to provide reasonable accommodation, as well asProhibition of unfair discriminatory treatment based on disability against persons with disabilities.This includes what is referred to as 'unjust discriminatory treatment', which is explained as follows by the Cabinet Office.
To deny or limit the provision of goods, services, and various opportunities to persons with disabilities without justifiable reasons, or to impose conditions that are not applied to non-disabled individuals, infringes upon the rights and interests of persons with disabilities.
Citation: Basic Policy on Advancing the Elimination of Discrimination Based on Disability (Cabinet Office)
In other words, for example,No national or local government or company can refuse or restrict service provision solely on the grounds of 'having a disability,' nor can they impose conditions only on persons with disabilities.Specific examples of prohibited unfair discriminatory treatment include cases such as the following.
◆ Unjust Discriminatory Treatment in Stores
・ A visually impaired person is refused entry to a restaurant with their guide dog on the grounds of a no-pets policy.
Refusing to respond to the request of a person with hearing impairments who says, 'I want to order by writing with the staff.'
・ Saying, 'Please come with a guardian or helper when you visit,' making the accompaniment of a helper a blanket condition for service provision.
◆ Unjust Discriminatory Treatment in Leisure Facilities
・ In a theme park, a wheelchair user is denied access to rides and attractions due to vague safety concerns that do not consider the type or severity of their disability.
・ A person with hearing impairments is excluded from guided tours because they cannot utilize audio guidance or announcements.
Despite not hindering business operations, they manage responses in a location different from that of persons without disabilities.
◆ Unjust Discriminatory Treatment in Schools
・ Refusing to allow applications or admission based on the presence of a disability.
・ Excluding students who require special support from general classes based on their disabilities.
◆ Unjust Discriminatory Treatment in Public Transportation
A wheelchair user attempted to board a bus but was refused by the driver on the grounds that 'it would be cumbersome.'
・ When persons with disabilities use a taxi, they are asked to pay more than the standard fare under the pretext of special services or assistance.
・ A visually impaired person is hindered in obtaining accurate information and safe movement due to a lack of audio guides and tactile paving at the station.
Such examples can act as barriers to the equal social participation of persons with disabilities. However, it is not necessarily the case that these acts can be definitively classified as illegal.It is important to note that if there is a justifiable reason, it would not be considered 'unjust discriminatory treatment'.This is the case.
However, this 'justifiable reason' does not simply mean that the business can claim something is reasonable,but must be recognized as 'justifiable' based on a comprehensive and objective assessment of specific circumstances from the perspectives of persons with disabilities, private businesses, and other third parties.This is necessary.
Next, let's introduce specific examples of providing reasonable accommodation.
Examples of Providing Reasonable Accommodation
Here, we will present specific examples of what providing reasonable accommodation might look like.
| Examples | Reasonable Accommodation | Type of Disability |
| In crowded places, a person with a disability may find it hard to stay calm and wait for their turn in places like government offices or hospital waiting rooms. | While securing a separate room is challenging, chairs can be moved to a space that is relatively shielded from view, or simple partitions can be used to block out some visibility in order to facilitate a calmer waiting experience. | Mental Disability |
| A person with hearing disabilities purchases a meal ticket at a restaurant, but cannot hear their number being called when the meal is ready. | The restaurant has displayed the number on an indoor monitor when it's called, or offered the option for staff to directly serve the meal when it’s ready. | Hearing Disability |
| Applications for legal consultations are only accepted via phone calls from the individual, but a person with hearing and language disabilities cannot make a call. | They enabled applications via email from the individual and provided sign language or written communication during consultations. | Hearing Disability Language Disability |
| They want to buy a product at a convenience store, but it’s their first time buying it, and they don't know where it is displayed or its price. | The store clerk guides them to the shelf and reads the price and packaging information of the desired product. | Visual Impairment |
| They want to apply for insurance but have a disability resulting from a severe illness that makes it difficult to write due to stiff hands. | Based on the applicant's wishes, the staff wrote on their behalf, ensuring the person's intentions were properly confirmed. At the same time, another staff member was present to verify the written content. | Internal Disabilities, Disabilities Due to Severe Illnesses |
| Due to swallowing difficulty, they cannot eat regular meals when dining out but wish to have the same menu items as their family as much as possible. | During the reservation, they were asked about their desired meal form, and the kitchen prepared it as closely as possible to the original menu while meeting dietary needs. | Severe Physical and Mental Disabilities |
What has been introduced is just a small part of the examples, and the reasonable accommodations that can be provided vary depending on the location and the situation. Therefore,When there is a request for accommodation, it is crucial to continuously work together with the opinions of the person involved or third parties to determine what accommodations can be made in line with the current status of the company.Posture is important.
Additionally, the Cabinet Office has published a collection of examples of reasonable accommodations that detail various cases based on different disabilities, so please refer to the following as well.
Reference Material:Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities [Collection of Examples of Reasonable Accommodation] (Cabinet Office)
The above has introduced examples of reasonable accommodations based on actual cases as a case study,Examples of actual initiatives by companiesare also presented.
Customer Support via FAX – SoftBank Corp.
At SoftBank, they have set up sign language support services and a dedicated fax inquiry line for customers with hearing disabilities or those who find phone inquiries difficult.They have established a sign language support desk as well as a dedicated fax inquiry desk.Additionally, chat support is available, making it easy to inquire via text through smartphones or computers.
Sign Language Support Store - KDDI Corporation
At au Style/au Shops and some Toyota au dealerships, simple writing boards have been installed to facilitate smoother communication with persons who are deaf or hard of hearing. Additionally,stores that offer sign language support and remote sign language service.are also listed.
Provision of 'Reasonable Accommodation' on Websites
Reasonable accommodation is also required of businesses that provide web services,to ensure web accessibility so that people with disabilities and the elderly can safely obtain information from websites.must be implemented.
To ensure web accessibility on their own websites and provide reasonable accommodation, companies mustbuild and improve their sites in accordance with established accessibility standards.This is necessary.The following article provides a detailed explanation of web accessibility and specific response methods.Thus, please refer to this article as well.
Reference article:What web accessibility measures must site managers implement?
If you're looking to reduce costs and construction time, 'UniWeb' is recommended.
Furthermore, web accessibility measures must be maintained and continued, which can be a significant burden for many companies implementing their own solutions. If a company's website is not compliant or if they are considering reducing operational burdens in the future, they should consider implementing our providedWeb Accessibility Tool 'UniWeb'We kindly ask you to consider the introduction of this.
UniWeb is a plugin-type tool that can easily incorporate various web accessibility features into any website, allowing for quick implementation by simply inserting a line of code.This tool makes it possible to implement compliant accessibility measures while significantly saving costs and timelines.This is its significant attraction.
◆ Accessibility features that can be implemented through UniWeb
With just one click, you can reflect accessibility features tailored to the characteristics of disabilities on your website.By clicking on the blue human icon in the lower right corner of this article, you can actually experience the features of UniWeb.so please give it a try.
There are no immediate penalties for violations, but there is a possibility of administrative guidance.
As discussed so far, the provision of reasonable accommodations is a legal obligation under the amended Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities, and it is also important to understand the penalties for violating this. First,In conclusion, there are no penalties for lack of compliance, and immediate penalties won't be imposed for non-compliance.
However, the authorities can provide necessary advice, guidance, and corrective recommendations to businesses that fail to provide reasonable accommodation despite requests from individuals with disabilities.Businesses are required to report on administrative guidance and recommendations, and failure to report or providing false reports may incur fines of up to 200,000 yen.In addition, if they do not comply with recommendations, this may be publicly disclosed.
Ifthis is made public, it could affect the company's social reputation.This should be a considerable concern, so businesses should adequately respond within a manageable range.
Less than 40% awareness of the revised law one year after its implementation
As of November 2025, more than one year has passed since the implementation of the revised Law for the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities last April; however, the situation highlights that reasonable accommodation is not fully recognized and practiced at the field level.
In a survey reported by Jiji Press in April 2025,36.4% of persons with disabilities "knew" that reasonable accommodation had become mandatory, while approximately 60% (63.6%) did not know.The reality that recognition on the part of the parties involved has not kept pace was demonstrated.
The government and local governments continue to hold information sessions and encourage groups to participate, but the Cabinet Office admits that "understanding has not deepened," and a lack of publicity remains a major issue.
In addition,With the acceleration of digitization, the number of "unusable situations" is rapidly increasing at a level prior to reasonable accommodation。
In another report by Jiji Press,Case of a visually impaired person with low vision who was confused by the self-checkout operation.are introduced, and "design barriers" such as no Braille, no readout, and no unified UI are left unaddressed.
The Japan Federation of Organizations of the Visually Impaired (2022 survey) also found that 68.4% of respondents were "troubled" by the digitization of government and businesses, andIn addition to self-checkout, the digital procedures of daily life themselves, such as image verification and one-time passwords for online banking, were also high barriers,Even as of 2025, there has been little progress in improving the level of improvement that can be felt by the parties concerned.。
Citation: Visually impaired people are confused by touch panels.
In light of the above, the current situation one year after enactment can be summarized as follows
◆Issues Remaining After One Year of Enforcement of the Revised Law
Digital facilities hinder accessibility and create new barriers.
Environmental improvement remains an obligation to make efforts, but the response is not keeping pace.
Reasonable accommodation cannot be covered by the system alone because it is individualized.
While the mandate for reasonable accommodation is an important step in itself, the reality is thatThe system has advanced, but the environment in which it can be used has not kept pace."The more digital contact points, such as online procedures, in-store services, and unmanned stores, in particular, the more pronounced the "environment lags behind".
Websites have the same structure, and accessibility cannot be achieved only by reasonable accommodations (individualized support)。
Contrast to ensure visibility
UI completed by keyboard operation
Maintenance of error messages and alternative text on forms
These are "environmental improvements" that should always be provided even if no reasonable accommodation is offered,Many companies have found it burdensome to develop accessibility support from scratch.。
Against the backdrop of these on-the-ground challenges,UniWeb for easy addition of web accessibility featuresThese tools can quickly create a foundation for reasonable accommodation, and are therefore a good solution to the current social issue of "lack of environmental improvement".
Conclusion
The amendment of the Act on the Elimination of Discrimination against Persons with Disabilities has made the provision of reasonable accommodations mandatory. However, for example, stores have not been legally obligated to design spaces that accommodate wheelchair users from the outset. This means that there is a situation where reasonable accommodations are mandated in environments where infrastructure is not yet sufficiently established, making it particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises.
However, it is also true that Japan is lagging in understanding people with disabilities and handicaps compared to the global standard, and if this continues, there is a possibility of deviating further from the world's standards. As a company, it is important to start with thorough hearings and to engage with persons with disabilities to deepen understanding of disabilities.
-
Contact Us
-
Request Info
-
Free Trial
-
Partner System







